Learning Outcomes
- Explain the 4 principles in the acronym FAIR
- Differentiate FAIR and OPEN science and application in training material
- Discuss the advantages of FAIR and OPEN training
What is FAIR and why do I care ?
1.1 Presentation
Here you can find the presentation for this session:
The full presentation can be downloaded here.
1.2 What is FAIR
In the Cambrige dictionary the word fair can stand for something that you expected or deserved, but I’d like to elaborate more about the acronym FAIR. In this case each letter stands for something different: _

_
I would say that expecting that training material is FAIR is just fair, don’t you agree?
Before you can decide if you agree or not maybe I should tell you more about each part of this acronym. From the need of reusing scholar data in research was born the idea of a consise and mesurable set of principles to endorse reusability, the FAIR principles. The idea is that those need to be available for humans but also in a machine readable format.
Challenge
Before looking for the answers below, try to answer with your current knowledge and perspective.
“How would you interpret each of this principles?”
Elaborate shortly how you see each of them (in general and for training) and then compare with the text below:
- Findable:
- Accessible:
- Interoperable:
- Reusable:
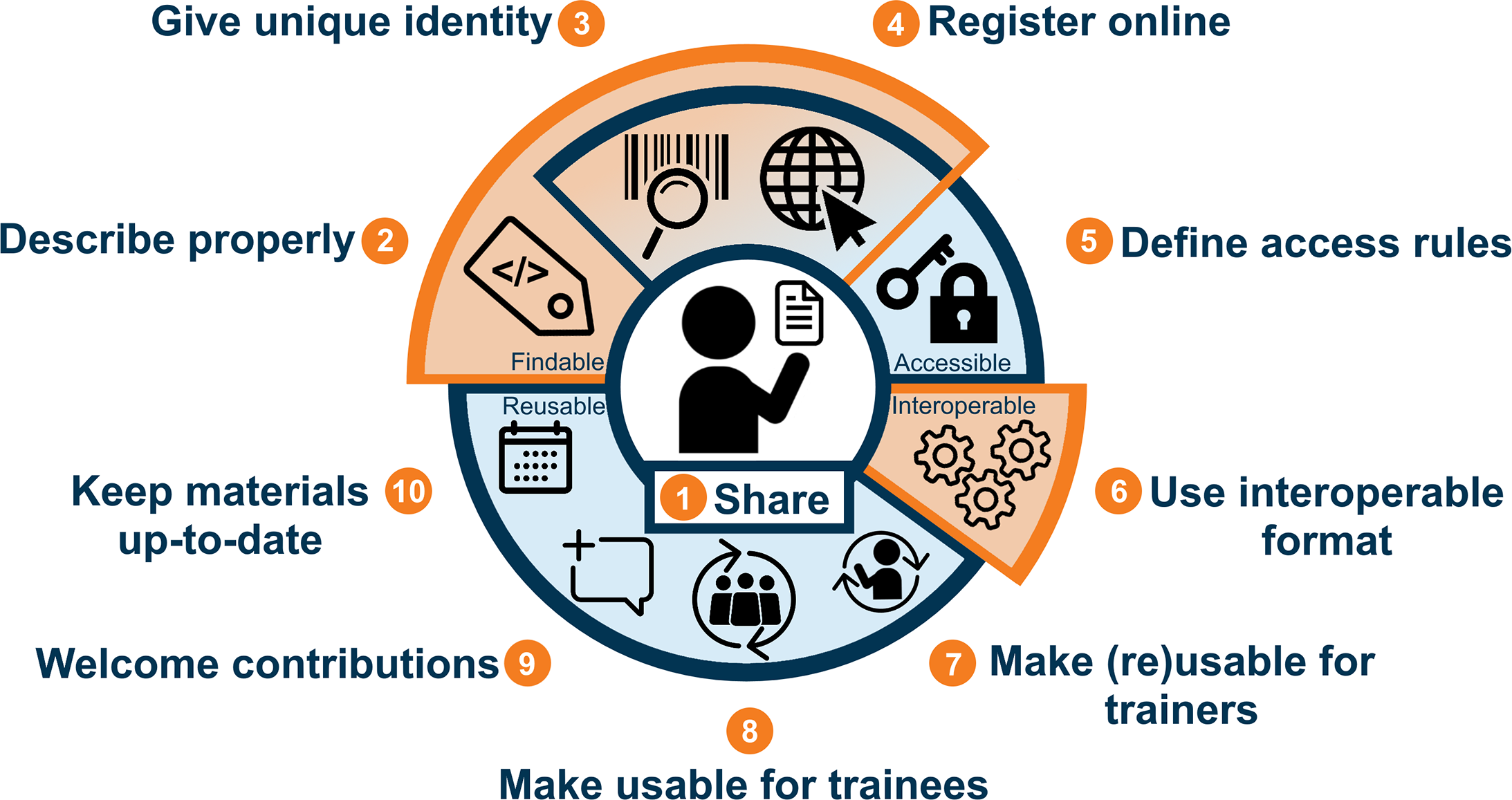
The main goal of the FAIR principals is to SHARE. For training material, this includes extending, updating and modifying the material to a certain audiance or circumstances. To achieve this final goal the four principals can be organized in 10 rules Garcia et al. 2020. Findable:
For data, including training material, to be considered FINDABLE we need to take in consideration three rules. First the material needs to be described in such a way that humans and machines can find the material and its metadata, it needs to have a unique identifier and to be registered online in a catalogue or repository.
Accessible:
To be considered ACCESSIBLE, the most importante thing is to define access rules. It can be through licenses, a document stating the access rules or a policy, any of those will allow the person who finds it to know how it can be accessed and what is authorized to do with the material like sharing, re-using, modifying. In some cases the material might be restricted or closed, but its metadata can still be found and the rules for the accessibility are clearly stated.
Interoperable:
Working as expected in different operational systems (OS) and different platforms is the main idea behind Interoperability ! For now I take the liberty to say that, maybe, this is level is more complicated for training material than it is for scientific data, just because we’ve been worring about it for longer when it comes to data analysis. But as you will see in the session for training material, there are several types of training material and some of them will be easy to open in any OS, but not easily editable, extended or updated. You must be asking yourself : “So what is the perfect solution?”, in this case several technical solutions are available to us, some are preferable but the interoperability will vary according to specific considerations as you will see later in this lesson.
Reusable:
After carefully considering all of the above, you want to reuse some material or make your material reusable. Consider when it comes to training that there are two main groups that can reuse the materials: (1) the trainers and (2) the trainees. So as trainers, we annotate, describe and make the material all as clear as possible so that other trainers or the trainees can read, listen or watch and know what you mean independently of your presence. And keep your material up-to-date! That is probably easier by welcoming contributions, by using a collaboration platform like GitHub or similar, and by making clear statements of how someone can contribute.
In case is not yet clear, all these steps also consider that the ones involved need to be acknowledged, as authors or contributors. Sharing material and reusing as much as possible needs to provide proper recognition mechanisms for those who dedicate their time and effort to do so, unless they assign a CC0 license or similar. But we will talk more about this in the following chapters.
_
_
Ten simple rules for making training materials FAIR. (Illustration from Luc Wiegers and Celia van Gelder:https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3593257.)
1.3 How is FAIR different compared OPEN ?
Now that you know a bit about what the acronym FAIR stands for, you can try to think about this question, how different are FAIR and OPEN?.
OPEN is related to the rules to access and share the material, clear rules will define if you can freely access, modify and share, or state that there are restrictions for a specific group. Access might be restricted through registration on a platform and the auhtors might add restrictions about how to share and with whom. There are many possibilities. Last but not least, it can have closed access and still be FAIR. You can find metadata, and information about it, but you cannot access the material.

From the course: RDM: your aly in your way to your publication
1.4 Why to create FAIR training material?
When you make your material FAIR you enable the community exchange while allowing this material to live beyond! Having FAIR materials makes it easier to share the content and maintain, update and reuse them by others. You also reinforce practices to ensure trainers and content creators recognition.